By Dr. Mercola
Vitamin D deficiency is pandemic in the United States, but many Americans, including physicians, are not aware that they may be lacking this important nutrient.
The video above may be one of the most important videos for you and your family's health this year.
I urge you to find some time to view it, so you can understand the nearly unbelievable benefits you will receive by understanding this vital nutrient.
In the second video, you will learn some important facts about sun exposure, as tanning incorrectly may indeed increase your risk of skin cancer...
For those of you who prefer to read your information, rather than watch it, I've summarized some of the most important points below.
But, again, please do take the time to watch the video lecture, as it has all the highly valuable details you need to know about vitamin D.
The Role of Vitamin D in Your Body
There are only about 30,000 genes in your body and vitamin D has been shown to influence about 3,000 of them.
That is one of the primary reasons it influences so many diseases, from cancer and autism to heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis, just to name a few.
Vitamin D isn't actually a vitamin, although scientists refer to it as such.
It's actually a steroid hormone that you get from sun exposure, food sources, and/or supplementation.
The term refers to either vitamin D2 or D3, but D3 (chemical name 25-hydroxy vitamin D) is real vitamin Dit's the same substance produced naturally through your skin by sun exposure.
Older research appears at odds on whether your body cares which form of D it's getting, but a study in the January 2011 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism1 found that D3 is 87 percent more effective than D2, and is the preferred form for treating vitamin D deficiency.2
Link Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Cancer Has Been Well-Tested and Confirmed
Theories linking vitamin D to certain cancers have been tested and confirmed in more than 200 epidemiological studies, and understanding of its physiological basis stems from more than 2,500 laboratory studies, according to epidemiologist Cedric Garland, DrPH, professor of family and preventive medicine at the UC San Diego School of Medicine. Here are just a few highlights into some of the most noteworthy findings:
- Some 600,000 cases of breast and colorectal cancers could be prevented each year if vitamin D levels among populations worldwide were increased, according to previous research by Dr. Garland and colleagues. And that's just counting the death toll for two types of cancer.
- Optimizing your vitamin D levels could help you to prevent at least 16 different types of cancer, including pancreatic, lung, ovarian, prostate, and skin cancers.
- A large-scale, randomized, placebo-controlled study on vitamin D and cancer showed that vitamin D can cut overall cancer risk by as much as 60 percent.3 This was such groundbreaking news that the Canadian Cancer Society has actually begun endorsing the vitamin as a cancer-prevention therapy.
- Light-skinned women who had high amounts of long-term sun exposure had half the risk of developing advanced breast cancer (cancer that spreads beyond your breast) as women with lower amounts of regular sun exposure, according to a study in the American Journal of Epidemiology.4
- A study by Dr. William Grant, Ph.D., internationally recognized research scientist and vitamin D expert, found that about30 percent of cancer deaths which amounts to two million worldwide and 200,000 in the United States could be prevented each year with higher levels of vitamin D.
Vitamin D has a protective effect against cancer in several ways, including:
- Increasing the self-destruction of mutated cells (which, if allowed to replicate, could lead to cancer)
- Reducing the spread and reproduction of cancer cells
- Causing cells to become differentiated (cancer cells often lack differentiation)
- Reducing the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, which is a step in the transition of dormant tumors turning cancerous
Beyond cancer, researchers have pointed out that increasing levels of vitamin D3 could prevent other chronic diseases that claim nearly one million lives throughout the world each year! Vitamin D also fights colds and the flu, as it regulates the expression of genes that influence your immune system to attack and destroy bacteria and viruses. In fact, it is very rare for someone with optimized vitamin D levels to come down with the flu.
Many Are Vitamin D Deficient
In the United States, the late winter average vitamin D is only about 15-18 ng/ml, which is considered a very serious deficiency state. Meanwhile, it's thought that over 95 percent of U.S. senior citizens may be deficient, along with 85 percent of the American public. Further:
- Vitamin D deficiency is epidemic in adults5 of all ages who have increased skin pigmentation, such as those whose ancestors are from Africa, the Middle East, or India, who always wear sun protection, or who limit their outdoor activities.
- African Americans and other dark-skinned people and those living in northern latitudes make significantly less vitamin D than other groups.
- 60 percent of people with type 2 diabetes have vitamin D deficiency.
- Studies showed very low levels of vitamin D among children, the elderly, and women.
- One U.S. study of women revealed that almost half of African American women of childbearing age might be vitamin D deficient.
Sun Exposure Is the BEST Way to Optimize Your Vitamin D Levels
The images used in this video belong to The United States Naval Observatory (USNO). To find the information for your area, please visit the USNO site.
Due to decades of professional and media misinformation, the typical American believes she should avoid the midday sun and need to use sunscreen before, and several times during, sun exposure. Unfortunately, this is a prescription for minimizing vitamin D levels and all its widely appreciated benefits. The video above provides practical guidelines on how to use natural sun exposure to optimize your vitamin D benefits.
To optimize your vitamin D level and get a healthy tan, it is important in the first few days to limit your exposure to the sun to allow your body's melanocyte cells to rev up the ability to produce protective pigmentation. Not only will this give you a tan, but it also serves to help protect you against overexposure to the sun. If you are a fairly light skinned individual that tends to burn, you will want to limit your initial exposure to a few minutes, especially if it is in the middle of summer.
The more tanned your skin gets, and/or the more tanned you want to become, the longer you can stay in the sun. If it is early or late in the season and/or you are a dark skinned individual, you could likely safely have 30 minutes on your initial exposure. If you are deeply pigmented and your immediate ancestors are from Africa, India or the Middle East, it is possible you may not even have to worry about the timing of your exposure.
Always err on the side of caution, however, and let it be your primary goal to never get sunburned.
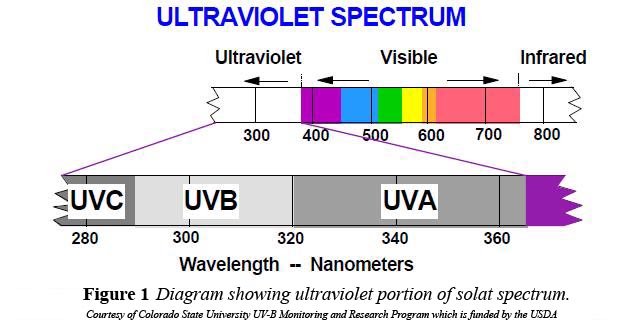
The key point to understand is that sunlight is composed of about 1,500 wavelengths, but the only wavelength that will have your body make vitamin D are UVB rays when they shine on unexposed skin. However, UVB rays from the sun have to pass through the atmosphere and reach where you are on Earth. This obviously does not occur in the winter for most of us, but the sun's rays are also impeded during a fair amount of the year for people living in temperate climates.
So, how do you know if you have entered into the summer season and into the time of year, for your location, where enough UVB is actually able to penetrate the atmosphere to allow for vitamin D production in your skin? It should be noted that this represents a very small portion of the total radiation from the sun that reaches the earth's surface. Much is filtered out by our atmosphere. So due to the physics and wavelength, UVB rays will only penetrate the atmosphere when the sun is above an angle of about 50° from the horizon. When the sun is lower than 50°, the ozone layer reflects the UVB rays but let through the longer UVA rays.
The first step is to determine the latitude and longitude of your location. You can easily do this on Google Earth, or if you are in the U.S. you can use the Latitude Longitude Calculator to find your latitude and longitude. Once you have obtained that you can go to the U.S. Navy site to calculate a table to determine the times and days of the year that the sun is above 50 degrees from the horizon. Find the US Naval Observatory Azimuth table here.
Translated to the date and time of some places on the globe, it means, for example: In my hometown of Chicago, the UVB rays are not potentially present until March 25, and by September 16th it is NOT possible to produce any vitamin D from the sun in Chicago. Please understand it is only theoretically possible to get UVB rays between those times. If it happens to be cloudy or raining, the clouds will also block the UVB rays.
From a health perspective it doesn't make much sense to expose your skin to the sun when it is lower than 50 degrees above the horizon because you will not receive any valuable UVB rays, and you will expose yourself to the more dangerous and potentially deadly UVA rays.
UVA's have a longer wavelength than UVB and can more easily penetrate the ozone layer and other obstacles (like clouds and pollution) on their way from the sun to the earth. UVA is what radically increases your risk of skin cancer and photoaging of your skin. So while it will give you a tan, unless the companion UVB rays are available, you're likely doing more harm than good and should probably stay out of the sun to protect your skin. During the times of the year when UVB rays are not present where you live, you essentially have two options: you can use a safe tanning bed or you can swallow oral vitamin D3.
For more detailed information about proper sun exposure, please see this article: "Little Sunshine Mistakes that Can Give You Cancer Instead of Vitamin D."
It's Not the Dosage that MattersIt's Your Blood Level
If for whatever reason you are unable to obtain adequate sun exposure or have access to a safe tannin bed, then it is strongly recommended that you use oral vitamin D supplementation. GrassrootsHealth is an organization primarily focused on creating awareness about the profound importance of vitamin D for optimal health. They're also developing and substantiating research to support the use of vitamin D as a prevention strategy against diseases like cancer.
There are currently 40 leading vitamin D experts from around the world on the GrassrootsHealth panel, and everyone agrees that the most important factor is the vitamin D serum level. There's no specific dosage level at which "magic" happens.
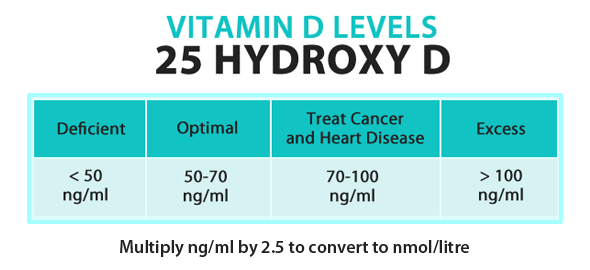
So while I will convey the recommended dosages in a moment, the most important message is that you need to take whatever dosage required to obtain a therapeutic level of vitamin D in your blood. The recommendations for optimal vitamin D levels have steadily increased over the past several years. In 2007, vitamin D experts recommended between 40 and 60 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). Since then, the optimal vitamin D level has been raised to 50-70 ng/ml, and when treating cancer or heart disease, as high as 70-100 ng/ml.
Fortunately, GrassrootsHealth has done the research and determined that the average dose of oral vitamin D that most adults need to reach 40 ng/ml is 8,000 IU's a day (bear in mind that 40 ng/ml is still below the updated level of 50-70 ng/ml, so you may need more than 8,000 IU's to reach optimal therapeutic levels.).
Getting the correct test is the first step in this process, as there are TWO vitamin D tests currently being offered: 1,25(OH)D, and 25(OH)D. The correct test your doctor needs to order is 25(OH)D, also called 25-hydroxyvitamin D, which is the better marker of overall D status. This is the marker that is most strongly associated with overall health. Next, the "normal" 25-hydroxyvitamin D lab range is 20-56 ng/ml. As you can see from the chart below, this conventional range is really a sign of deficiency, and is too broad to be ideal. In fact, your vitamin D level should never be below 32 ng/ml, and any levels below 20 ng/ml are considered serious deficiency states.
The OPTIMAL value that you're looking for is 50-70 ng/ml, and this range applies for everyone: children, adolescents, adults, and seniors.
Keeping your vitamin D level within the optimal range, and even erring toward higher vitamin D numbers, is going to give you the most protective benefit. And the way you maintain your levels within this range is by getting tested regularly -- say two to four times a year in the beginning, and adjusting your vitamin D intake accordingly.
Crucial Information About Vitamin D Testing That You NEED to Know
One of the most important things to keep in mind if you opt for oral supplementation is that you only want to supplement with natural vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which is human vitamin D. Do NOT use the synthetic and highly inferior vitamin D2. This is typically prescribed by many well intentioned doctors who seek to take advantage of a patient's prescription coverage. Unfortunately this form is FAR more expensive than the real vitamin D3, which is one of the least expensive vitamins we have. But more importantly it does not work nearly as well as D3 and can actually block the real D3 from working properly.
Bottom line: ONLY use vitamin D3 when supplementing.
GrassrootsHealth has greatly contributed to the current knowledge on vitamin D through what's called the D* Action Study. They published their first paper in 2011, which includes data on about 3,500 people. One interesting finding is that it's not nearly as easy to reach toxic levels with oral vitamin D3 supplementation as previously thought. According to Carole Baggerly:
" One very significant thing shown by this research was that even with taking the supplement, the curve for the increase in the vitamin D level is not linear. It is curvilinear and it flattens, which is why it's even hard to get toxic with a supplement."
As mentioned earlier, based on this research, it now appears as though most adults need about 8,000 IU's of vitamin D a day in order to get their serum levels above 40 ng/ml. Not only is this significantly higher than previous vitamin D recommendations, but this also means that even if you do not regularly monitor your vitamin D levels, your risk of overdosing is going to be fairly slim, even if you take as much as 8,000 IU's a day. That said, I still advocate getting your vitamin D levels tested regularly.
For an in-depth explanation of what you need to know before you get tested, please read my article Test Values and Treatment for Vitamin D Deficiency. If you are in the U.S. the primary lab you want to use is Lab Corp.
To learn more about the latest research on vitamin D, please listen to my interview with Carole Baggerly below, which was taped in late 2011.
Download Interview Transcript
